Active Recall and Spaced Repetition with Recall
Learning is an integral part of our lives. Whether we're students, professionals, or curious souls, we all spend a good deal of time acquiring new knowledge. From watching tutorials on YouTube to consuming online articles we're in constant pursuit of knowledge. As we stumble upon valuable pieces of information, we take notes and diligently save them in our personal knowledge base.
But, here's a question: how often do you revisit the content you've stored away? If your answer is "not as often as I'd like", then you are not alone. This is where the Recall Review tool comes into play.
The Recall Review is a tool designed to help you review and consolidate the knowledge stored in your knowledge base using scientifically backed techniques known as Active Recall and Spaced Repetition. By integrating Spaced Repetition, the tool ensures your saved content in your knowledge base is revisited at optimal intervals, boosting long-term retention. Meanwhile, its incorporation of Active Recall principles challenges you to actively test and reinforce your understanding of the saved content, ensuring a deeper grasp of the information.

What are Active Recall and Spaced Repetition?
In the vast landscape of learning techniques, two strategies stand out for their effectiveness and scientific backing: Active Recall and Spaced Repetition. While each is powerful on its own, when combined, they form a formidable duo that can significantly enhance memory retention and understanding.
Active Recall: Engaging the Brain
At its core, Active Recall is about testing yourself. Instead of passively reading and re-reading information, which can create an illusion of knowledge, Active Recall challenges you to remember information without looking at the source. This is often done by answering questions about the source material.
Active Recall is a reflection of how our brains are wired. When we actively retrieve information, we strengthen the neural pathways associated with that knowledge. This concept is supported by The Testing Effect, a phenomenon observed in numerous studies. Research has shown that the act of recalling information, as opposed to passive review, enhances long-term retention. One seminal study by Roediger and Karpicke (2006) found that students who practiced retrieval (i.e., tested themselves) retained 80% of the material after a week, while those who used passive study methods retained only 34%.
Spaced Repetition: Timing is Everything
Spaced Repetition is a technique that involves reviewing information at increasing intervals over time. The idea is rooted in the understanding of our brain's 'forgetting curve', which shows that newly acquired information is forgotten rapidly unless it's reviewed.
The Forgetting Curve
The forgetting curve, first conceptualized by Hermann Ebbinghaus in the 19th century, illustrates how information is lost over time when there's no attempt to retain it. According to Ebbinghaus, memory retention experiences a sharp decline after initial learning, but the rate of decline decreases over time.
However, Ebbinghaus also discovered something crucial: this forgetting curve could be flattened with a repeated review of the learned material. Every time a review occurs, the information gets more embedded in our long-term memory, reducing the rate at which we forget.
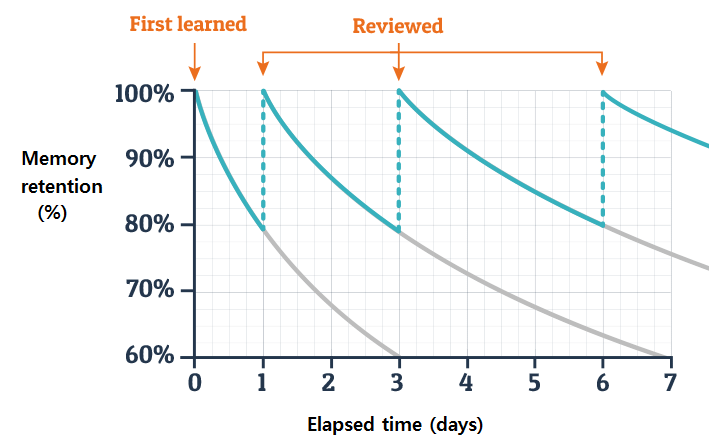
The graph above demonstrates a typical forgetting curve and how spaced repetition counters it. The curve drops sharply after the first learning event, indicating that our memory of the new information decreases rapidly. However, when we review the information (represented by the points on the curve), the rate of memory decline lessens. Each review resets the forgetting curve, and it becomes less steep (indicating slower forgetting) and shifts to the right (indicating longer intervals before forgetting). Over time and with regular reviews, information transitions from our short-term memory to our long-term memory.
Modern research continues to validate Ebbinghaus's findings. A study by Cepeda et al. (2008) found that spacing out reviews over increasing intervals (as opposed to massed or crammed study sessions) significantly improves long-term retention. The study concluded that optimal retention is achieved when reviews are spaced out in a manner that aligns with the individual's forgetting curve.
The Synergy of Active Recall and Spaced Repetition
While both Active Recall and Spaced Repetition have their individual merits, their combined application offers a synergistic effect. By actively retrieving information at strategically spaced intervals, you can harness the best of both worlds, ensuring that knowledge is not only retained but is also easily accessible.
Applying Active Recall and Spaced Repetition using Recall
In today's digital age, the Internet is a treasure trove of knowledge, with countless articles, videos, and resources available at our fingertips. But how do we ensure that the information we consume online doesn't just pass through our minds like water through a sieve? The Recall Review offers a solution, seamlessly integrating the principles of Active Recall and Spaced Repetition with any online content you wish to retain.
Here is a step-by-step Guide to using Recall Review:
Step 1: Collect content you want to learn from
Using The Recall Browser Extension you can create knowledge cards from any blog posts, Wikipedia pages, YouTube videos or any other webpages.
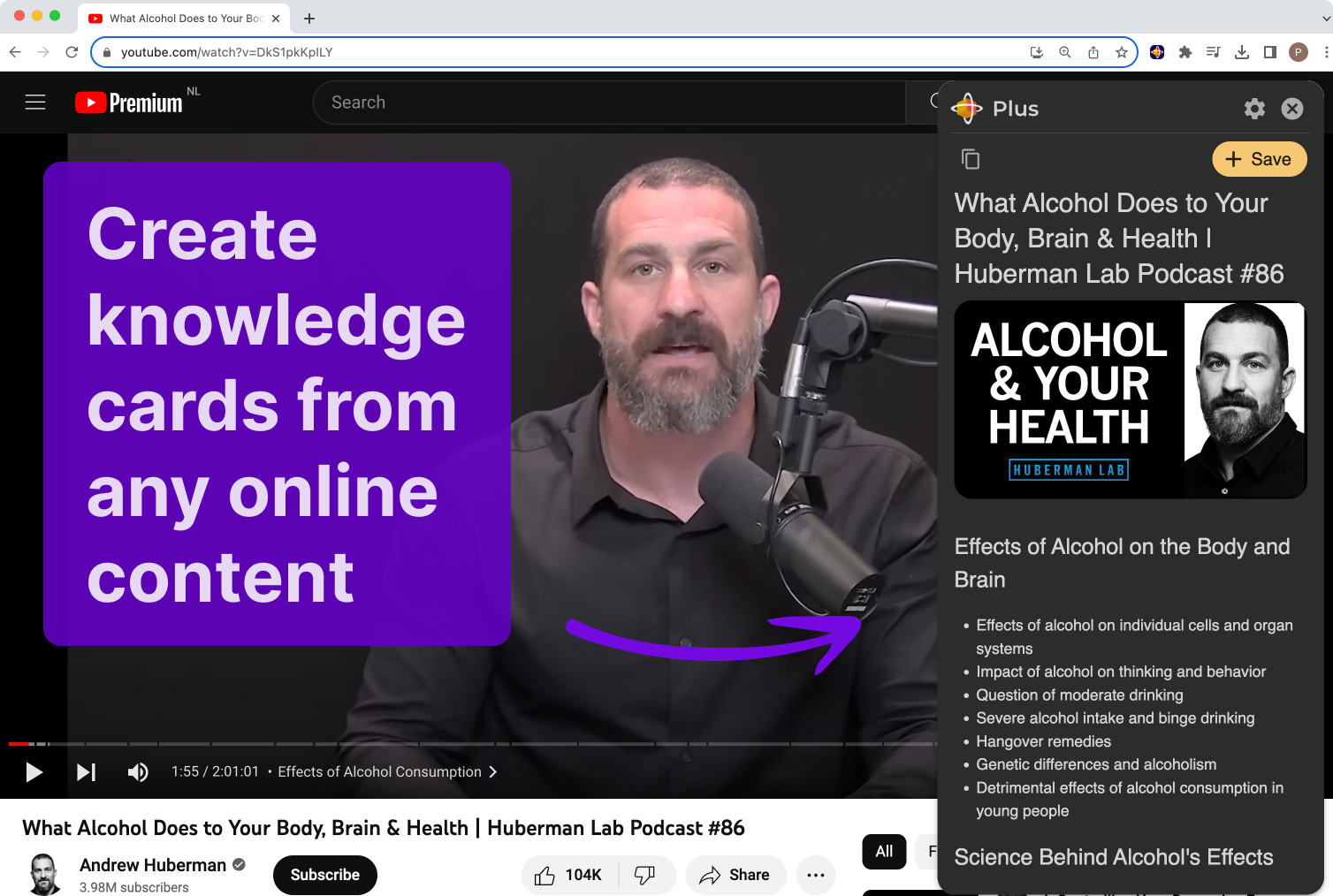
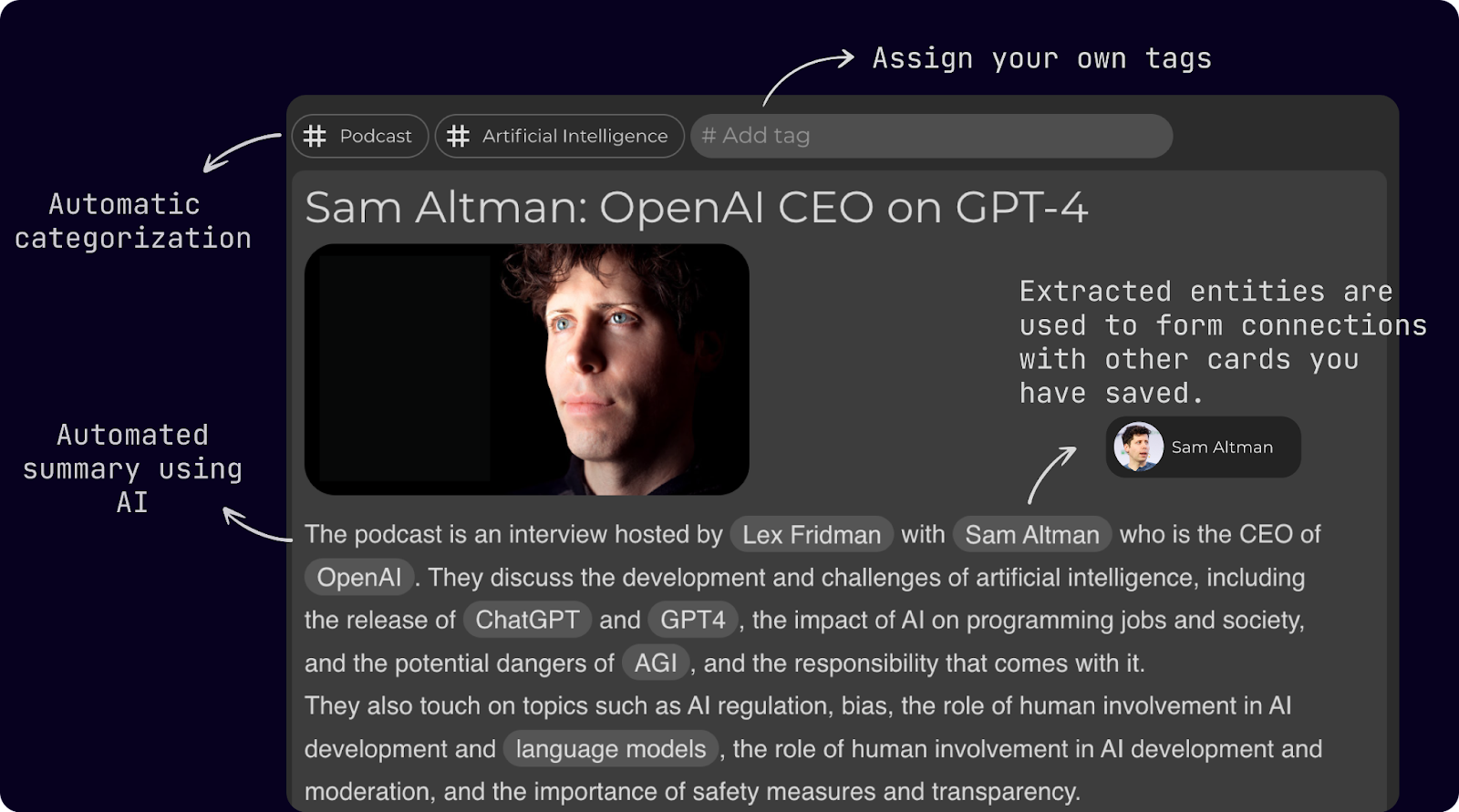
What is a Knowledge Card?
A knowledge card is a concise summary of information about a specific topic. It could be from a blog post, YouTube video, podcast, recipe or anything else you find online. The knowledge card gets automatically categorized in your knowledge base and connected with other cards that you have saved in the past.
Step 2: Start Your Review
When you're ready to review the knowledge cards that you have saved, Recall will curate a set of 10 cards from your knowledge base. These aren't randomly selected, they're chosen based on your personal spaced repetition schedule, ensuring that you're reviewing content at the optimal time for retention.
Step 3: Review your Knowledge Cards
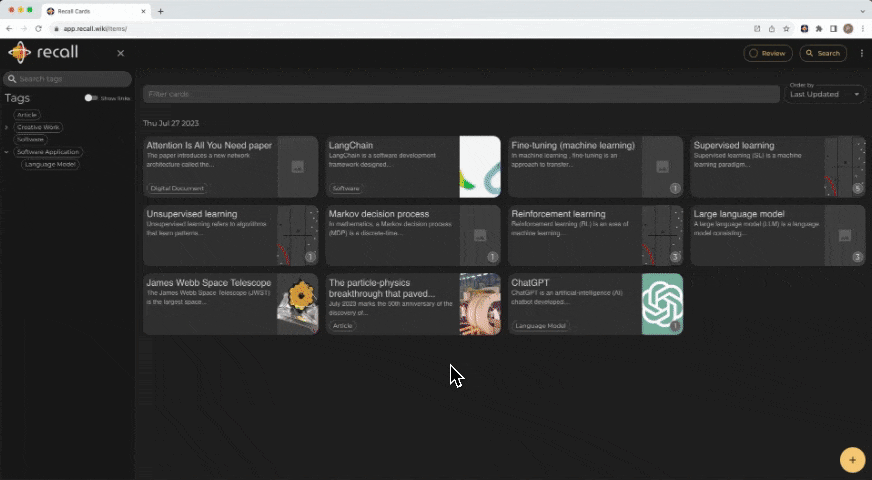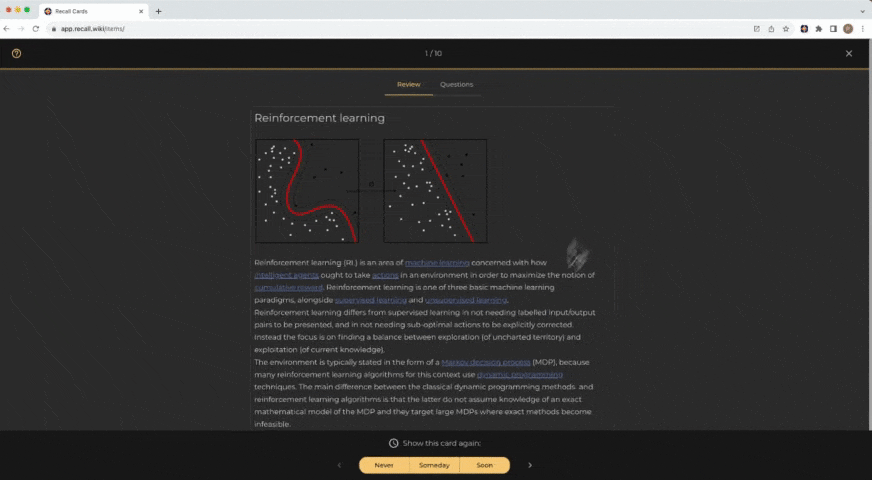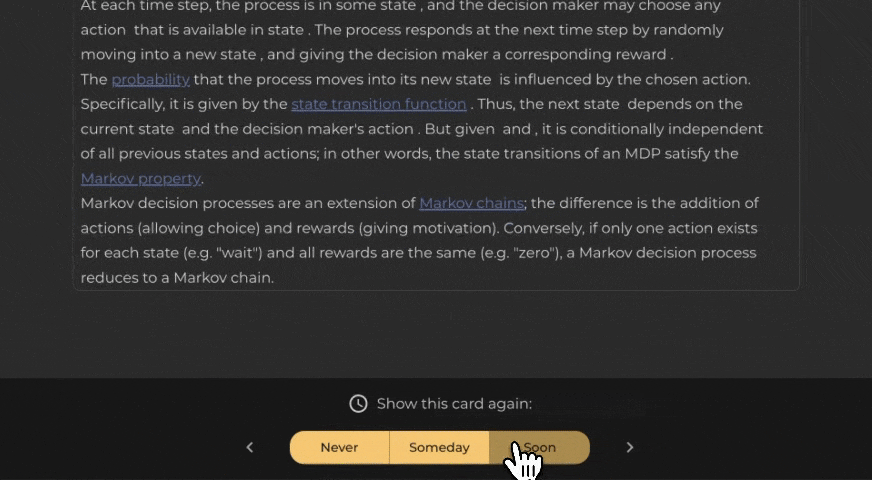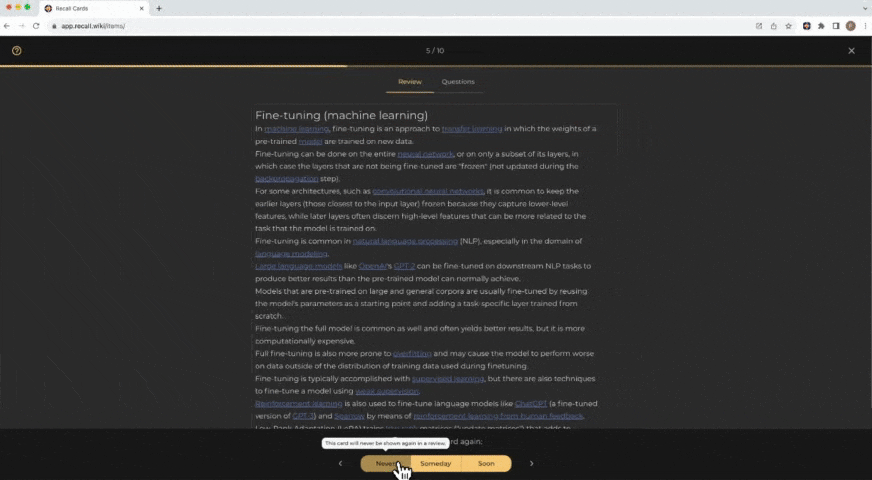
Go through each knowledge card in the review one-by-one and review its content. Once you're done, you can provide feedback to Recall based on how well you feel that you have remembered the card's content. This feedback will be used by Recall to determine how long until the card should be reviewed again. The options are:
- Soon: Choose this if you struggle to recall the card's information and would like to review it soon.
- Someday: If you remember the card's content but wish to revisit it in the future, select this.
- Never: Opt for this when you have entirely memorized the card's content and do not wish to review it again.
Step 4: Active Recall with AI Generated Questions
The next step is to test what you have learned from the review with Active Recall. Recall will use AI to generate questions based on the content in the cards you just reviewed. Once you've answered all questions, click "Check Answers" to verify your responses. Depending on your performance, you can choose to retry the questions or proceed to the next card.
Step 5: Track Your Progress
After completing your review and Active Recall questions, you can see the total number of cards left for revision. This keeps you informed about your progress and helps you plan your future reviews.
The Benefits of using Recall for Active Recall and Spaced Repetition
While many learning techniques come and go, Active Recall and Spaced Repetition have stood the test of time, and for good reason. These methods, rooted deeply in cognitive science, offer a range of benefits that can transform the way we retain information. Besides the primary benefit of improved information retention, here are some other benefits you can expect to see when you practice Active Recall and Spaced Repetition with Recall.
Saving time
Instead of re-reading material multiple times (which often yields diminishing returns), these techniques prioritize active engagement and timely review. This ensures that each minute spent studying is productive, reducing the overall time required to master a topic.
Reduced Cognitive Load
By breaking down learning sessions into focused intervals and actively engaging with the material, these techniques reduce the cognitive strain often associated with long, passive study sessions. This makes learning more enjoyable and sustainable.
Versatility Across Topics
Whether it's a complex scientific article, a podcast, or an online tutorial, Recall Review's system is adaptable. Its ability to create cards from diverse online content means users can apply Active Recall and Spaced Repetition to virtually any content they find online.
Promotion of Deep Understanding
Active Recall pushes you to understand concepts at a deeper level. It's one thing to recognize a correct answer and another to retrieve it from memory. This depth of understanding aids in connecting new knowledge to existing knowledge, promoting holistic learning.
Other Spaced Repetition Tools
No blog post about spaced repetition would be complete without acknowledging some of the original tools that have been around for years. These tools, each with its own merits, have paved the way for modern innovations like Recall. Below I will describe the pros and cons of each of these platforms.
Anki
Pros
Anki stands out for its high customization and effective spaced repetition algorithm. A vast community supports it, offering shared card decks on a myriad of topics. Its cross-platform nature ensures accessibility on various devices.
Cons
New users might find Anki's interface daunting, and creating your own cards can be time-consuming. The user experience feels less modern compared to newer apps. While shared decks are abundant, their quality can be inconsistent.
Quizlet
Pros
Quizlet is celebrated for its user-friendly and modern interface, making it a favorite among the younger generation. The platform promotes collaborative learning, allowing users to both share their own sets and access those created by others.
Cons
Quizlet does have its limitations. Its structured templates for creating study sets can sometimes feel restrictive compared to Anki, especially for those seeking a more nuanced content capture. Just like in Anki, creating your own cards can be tedious and time-consuming.
SuperMemo
Pros
SuperMemo is known for its advanced spaced repetition algorithm, which has been honed over decades of research to optimize review schedules.
Cons
SuperMemo's strengths can also be its weaknesses for some users. The platform's comprehensive features can present a steep learning curve for newcomers. Additionally, in comparison to some of the newer platforms on the market, SuperMemo's interface can feel a bit dated, lacking the intuitive design that many modern users have come to expect. And just like Quizlet and Anki, creating your own cards can be tedious and time-consuming.
The Recall Review
Recall is taking a new approach leveraging the latest advancements in AI to allow the user to seamlesses generate cards and questions from any online content they find interesting. Whether it's a Youtube video, Podcast, blog post or Wikipedia article Recall's browser extension can create a card from it.
While Recall offers features that students might find beneficial, the flexibility in the content that you can integrate makes it appealing to a much wider audience. Anyone who considers themselves a lifelong learner can use Recall for continuous learning and personal growth.
In conclusion, the Recall Review tool is a powerful ally in your learning journey. It empowers you to revisit and consolidate your knowledge, helping you transform information into long-lasting wisdom. Whether you're a student preparing for exams or a professional keen to keep your knowledge fresh, embrace the Recall Review tool and make your learning more efficient, effective, and enjoyable.